R 二项分布
二项分布模型处理在一系列实验中仅发现两个可能结果的事件的成功概率。 例如,掷硬币总是给出头或尾。 在二项分布期间估计在10次重复抛掷硬币中精确找到3个头的概率。
R语言有四个内置函数来生成二项分布。 它们描述如下。
dbinom(x, size, prob)pbinom(x, size, prob)qbinom(p, size, prob)rbinom(n, size, prob)
以下是所使用的参数的描述
x是数字的向量。
p是概率向量。
n是观察的数量。
size是试验的数量。
prob是每个试验成功的概率。
dbinom()
该函数给出每个点的概率密度分布。
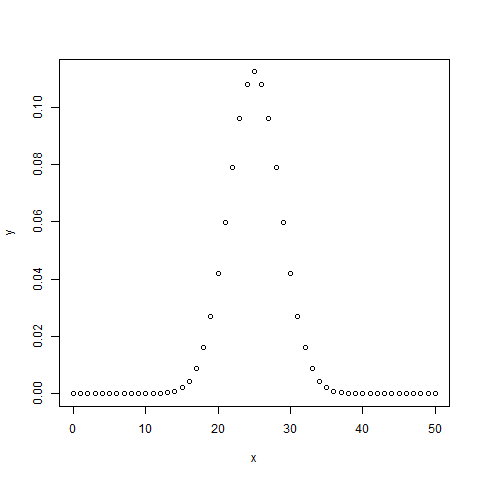
# Create a sample of 50 numbers which are incremented by 1.x <- seq(0,50,by = 1)# Create the binomial distribution.y <- dbinom(x,50,0.5)# Give the chart file a name.png(file = "dbinom.png")# Plot the graph for this sample.plot(x,y)# Save the file.dev.off()
当我们执行上面的代码,它产生以下结果:
pbinom()
此函数给出事件的累积概率。 它是表示概率的单个值。
# Probability of getting 26 or less heads from a 51 tosses of a coin.x <- pbinom(26,51,0.5)print(x)
当我们执行上面的代码,它产生以下结果:
[1] 0.610116
qbinom()
该函数采用概率值,并给出累积值与概率值匹配的数字。
# How many heads will have a probability of 0.25 will come out when a coin is tossed 51 times.x <- qbinom(0.25,51,1/2)print(x)
当我们执行上面的代码,它产生以下结果:
[1] 23
rbinom()
该函数从给定样本产生给定概率的所需数量的随机值。
# Find 8 random values from a sample of 150 with probability of 0.4.x <- rbinom(8,150,.4)print(x)
当我们执行上面的代码,它产生以下结果:
[1] 58 61 59 66 55 60 61 67