Perl 数据库连接
本章节我们将为大家介绍 Perl 数据库的连接。
Perl 5 中我们可以使用 DBI 模块来连接数据库。
DBI 英文全称:Database Independent Interface,中文称为数据库独立接口。
DBI 作为 Perl 语言中和数据库进行通讯的标准接口,它定义了一系列的方法,变量和常量,提供一个和具体数据库平台无关的数据库持久层。
DBI 结构
DBI 和具体数据库平台无关,我们可以将其应用在Oracle, MySQL 或 Informix, 等数据库中。
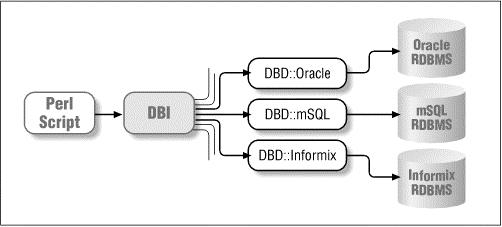
图表中 DBI 获取所有 API(Application Programming Interface:应用程序接口) 发送过来的 SQL 数据,然后分发到对应的驱动上执行,最后再获取数据返回。
变量名约定
以下设置了比较常用的变量名命名方法:
$dsn 驱动程序对象的句柄$dbh 一个数据库对象的句柄$sth 一个语句或者一个查询对象的句柄$h 通用的句柄 ($dbh, $sth, 或 $drh),依赖于上下文$rc 操作代码返回的布什值(true 或 false)$rv 操作代码返回的整数值@ary 查询返回的一行值的数组(列表)$rows 操作代码返回的行数值$fh 文件句柄undef NULL 值表示未定义\%attr 引用属性的哈希值并传到方法上
数据库连接
接下来我们以 MySQL 数据库为例演示 Perl 是如何对数据库进行操作的。
这里我们在 MySQL 数据库创建 test 数据库,数据表为 Websites,创建表结构及数据如下所示:
SET NAMES utf8;SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;-- ------------------------------ Table structure for `websites`-- ----------------------------DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `websites`;CREATE TABLE `websites` (`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`name` char(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '站点名称',`url` varchar(255) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',`alexa` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT 'Alexa 排名',`country` char(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '国家',PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=8 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;-- ------------------------------ Records of `websites`-- ----------------------------BEGIN;INSERT INTO `websites` VALUES ('1', 'Google', 'https://www.google.cm/', '1', 'USA'), ('2', '淘宝', 'https://www.taobao.com/', '13', 'CN'), ('3', 'baidu', 'http://www.baidu.com/', '5000', 'USA'), ('4', '微博', 'http://weibo.com/', '20', 'CN'), ('5', 'Facebook', 'https://www.facebook.com/', '3', 'USA'), ('7', 'stackoverflow', 'http://stackoverflow.com/', '0', 'IND');COMMIT;SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
接下来我们使用以下代码来连接数据库:
#!/usr/bin/perl -wuse strict;use DBI;my $host = "localhost"; # 主机地址my $driver = "mysql"; # 接口类型 默认为 localhostmy $database = "test"; # 数据库# 驱动程序对象的句柄my $dsn = "DBI:$driver:database=$database:$host";my $userid = "root"; # 数据库用户名my $password = "123456"; # 数据库密码# 连接数据库my $dbh = DBI->connect($dsn, $userid, $password ) or die $DBI::errstr;my $sth = $dbh->prepare("SELECT * FROM Websites"); # 预处理 SQL 语句$sth->execute(); # 执行 SQL 操作# 注释这部分使用的是绑定值操作# $alexa = 20;# my $sth = $dbh->prepare("SELECT name, url# FROM Websites# WHERE alexa > ?");# $sth->execute( $alexa ) or die $DBI::errstr;# 循环输出所有数据while ( my @row = $sth->fetchrow_array() ){print join('\t', @row)."\n";}$sth->finish();$dbh->disconnect();
插入操作
执行步骤:
- 使用 prepare() API 预处理 SQL 语句。
- 使用 execute() API 执行 SQL 语句。
- 使用 finish() API 释放语句句柄。
- 最后如果一切顺利就会提交以上执行操作。
my $sth = $dbh->prepare("INSERT INTO Websites(name, url, alexa, conutry )values('Twitter', 'https://twitter.com/', 10, 'USA')");$sth->execute() or die $DBI::errstr;$sth->finish();$dbh->commit or die $DBI::errstr;
应用程序还可以绑定输出和输入参数,下面例子通过用变量 取代 ? 占位符的位置来执行一条插入查询:
my $name = "Twitter";my $url = "https://twitter.com/";my $alexa = 10;my $conutry = "USA";my $sth = $dbh->prepare("INSERT INTO Websites(name, url, alexa, conutry )values(?,?,?,?)");$sth->execute($name,$url,$alexa, $conutry)or die $DBI::errstr;$sth->finish();$dbh->commit or die $DBI::errstr;
更新操作
执行步骤:
- 使用 prepare() API 预处理 SQL 语句。
- 使用 execute() API 执行 SQL 语句。
- 使用 finish() API 释放语句句柄。
- 最后如果一切顺利就会提交以上执行操作。
my $sth = $dbh->prepare("UPDATE WebsitesSET alexa = alexa + 1WHERE country = 'CN'");$sth->execute() or die $DBI::errstr;print "更新的记录数 :" + $sth->rows;$sth->finish();$dbh->commit or die $DBI::errstr;
应用程序还可以绑定输出和输入参数,下面例子通过用变量取代 ? 占位符的位置来执行一条更新查询:
$name = 'Perl 教程';my $sth = $dbh->prepare("UPDATE WebsitesSET alexa = alexa + 1WHERE name = ?");$sth->execute('$name') or die $DBI::errstr;print "更新的记录数 :" + $sth->rows;$sth->finish();
当然我们也可以绑定要设置的值,如下所示将 country 为 CN 的 alexa 都修改为 1000:
$country = 'CN';$alexa = 1000:;my $sth = $dbh->prepare("UPDATE WebsitesSET alexa = ?WHERE country = ?");$sth->execute( $alexa, '$country') or die $DBI::errstr;print "更新的记录数 :" + $sth->rows;$sth->finish();
删除数据
执行步骤:
- 使用 prepare() API 预处理 SQL 语句。
- 使用 execute() API 执行 SQL 语句。
- 使用 finish() API 释放语句句柄。
- 最后如果一切顺利就会提交以上执行操作。
以下数据将 Websites 中 alexa 大于 1000 的数据都删除:
$alexa = 1000;my $sth = $dbh->prepare("DELETE FROM WebsitesWHERE alexa = ?");$sth->execute( $alexa ) or die $DBI::errstr;print "删除的记录数 :" + $sth->rows;$sth->finish();$dbh->commit or die $DBI::errstr;
使用 do 语句
do 语句可以执行 UPDATE, INSERT, 或 DELETE 操作,使用他比较简短,执行成功返回true,执行失败返回 false,实例如下:
$dbh->do('DELETE FROM Websites WHERE alexa>1000');
COMMIT 操作
commit 为提交事务,完成数据库的操作:
$dbh->commit or die $dbh->errstr;
ROLLBACK 操作
如果在 SQL 执行过程中发生错误,可以回滚数据,不做任何改变:
$dbh->rollback or die $dbh->errstr;
事务
和其它的语言一样, perl DBI对数据库的操作也支持事务处理, 它的实现方式有两个:
1、 在连接数据库的时候就开始一个事务
$dbh = DBI->connect($dsn, $userid, $password, {AutoCommit => 0}) or die $DBI::errstr;
以上代码在连接的时候设置了AutoCommit为false, 也就是说当你对数据库进行更新操作的时候, 它不会自动地把那些更新直接写到数据库里, 而是要程序通过 $dbh->commit 来使数据真正地写到数据库里, 或 $dbh->rollback 来回滚刚才的操作。
2、 通过$dbh->begin_work()语句来开始一个事务
这种方式就不需要在连接数据库的时候设置 AutoCommit = 0 。
可以一次数据库连接进行多次事务操作, 不用每一次事务的开始都去连接一次数据库。
$rc = $dbh->begin_work or die $dbh->errstr;#######################这里执行一些 SQL 操作#####################$dbh->commit; # 成功后操作-----------------------------$dbh->rollback; # 失败后回滚
断开数据库连接
如果我们需要断开数据库连接,可以使用 disconnect API:
$rc = $dbh->disconnect or warn $dbh->errstr;