XML DOM 定位节点
可通过使用节点间的关系对节点进行定位。
实例
下面的例子使用 XML 文件 books.xml。
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
- <bookstore>
- <book category="children">
- <title lang="en">Harry Potter</title>
- <author>J K. Rowling</author>
- <year>2005</year>
- <price>29.99</price>
- </book>
- <book category="cooking">
- <title lang="en">Everyday Italian</title>
- <author>Giada De Laurentiis</author>
- <year>2005</year>
- <price>30.00</price>
- </book>
- <book category="web">
- <title lang="en">Learning XML</title>
- <author>Erik T. Ray</author>
- <year>2003</year>
- <price>39.95</price>
- </book>
- <book category="web">
- <title lang="en">XQuery Kick Start</title>
- <author>James McGovern</author>
- <author>Per Bothner</author>
- <author>Kurt Cagle</author>
- <author>James Linn</author>
- <author>Vaidyanathan Nagarajan</author>
- <year>2003</year>
- <price>49.99</price>
- </book>
- </bookstore>
函数 loadXMLDoc(),位于外部 JavaScript 中,用于加载 XML 文件。
获取节点的父节点
本例使用 parentNode 属性来获取节点的父节点。
<html><head><script type="text/javascript" src="/example/xdom/loadxmldoc.js"></script></head><body><script type="text/javascript">xmlDoc=loadXMLDoc("/example/xdom/books.xml");x=xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("book")[0];document.write(x.parentNode.nodeName);</script></body></html>
获取节点的首个子节点
本例使用 firstChild() 方法和一个自定义函数来获取一个节点的首个子节点。
<html><head><script type="text/javascript" src="/example/xdom/loadxmldoc.js"></script><script type="text/javascript">//check if the first node is an element nodefunction get_firstChild(n){y=n.firstChild;while (y.nodeType!=1){y=y.nextSibling;}return y;}</script></head><body><script type="text/javascript">xmlDoc=loadXMLDoc("/example/xdom/books.xml");x=get_firstChild(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("book")[0]);document.write(x.nodeName);</script></body></html>
定位 DOM 节点
通过节点间的关系访问节点树中的节点,通常称为定位节点 ("navigating nodes")。
在 XML DOM 中,节点的关系被定义为节点的属性:
- parentNode
- childNodes
- firstChild
- lastChild
- nextSibling
- previousSibling
下面的图像展示了 (books.xml) 中节点树的一个部分,并说明了节点之间的关系:
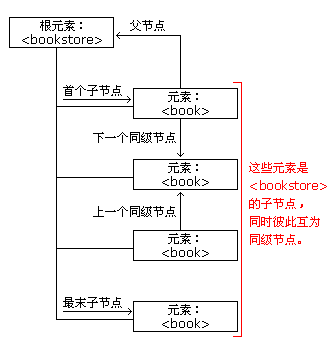
DOM - 父节点
所有的节点都仅有一个父节点。下面的代码定位到 <book> 的父节点:
- xmlDoc=loadXMLDoc("books.xml");
- x=xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("book")[0];
- document.write(x.parentNode.nodeName);
例子解释:
- 通过使用 loadXMLDoc() 把 "books.xml" 载入到 xmlDoc 中
- 获取第一个 <book> 元素
- 输出 "x" 的父节点的节点名
避免空的文本节点
Firefox,以及其他一些浏览器,把空的空白或换行当作文本节点,而 IE 不会这么做。
这会在使用下列属性使产生一个问题:firstChild、lastChild、nextSibling、previousSibling。
为了避免定位到空的文本节点(元素节点之间的空格和换行符号),我们使用一个函数来检查节点的类型:
- function get_nextSibling(n)
- {
- y=n.nextSibling;
- while (y.nodeType!=1)
- {
- y=y.nextSibling;
- }
- return y;
- }
有了上面的函数,我们就可以使用 get_nextSibling(node) 来代替 node.nextSibling 属性。
代码解释:
元素节点的类型是 1。如果同级节点不是元素节点,就移动到下一个节点,直到找到元素节点为止。通过这个办法,在 IE 和 Firefox 中,都可以得到相同的结果。
获取第一个元素
下面的代码显示第一个 <book> 的第一个元素节点:
- <html>
- <head>
- <script type="text/javascript" src="loadxmldoc.js">
- </script>
- <script type="text/javascript">
- //check if the first node is an element node
- function get_firstChild(n)
- {
- y=n.firstChild;
- while (y.nodeType!=1)
- {
- y=y.nextSibling;
- }
- return y;
- }
- </script>
- </head>
- <body>
- <script type="text/javascript">
- xmlDoc=loadXMLDoc("books.xml");
- x=get_firstChild(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("book")[0]);
- document.write(x.nodeName);
- </script>
- </body>
- </html>
输出:
- title
例子解释:
- 通过使用 loadXMLDoc() 把 "books.xml" 载入 xmlDoc 中
- 在第一个 <book> 上使用 get_firstChild 函数,来获取元素节点中的第一个子节点
- 输出第一个子节点(属于元素节点)的节点名
实例
下面的例子使用相似的函数:
firstChild
<html><head><script type="text/javascript" src="/example/xdom/loadxmldoc.js"></script><script type="text/javascript">//check if the first node is an element nodefunction get_firstChild(n){y=n.firstChild;while (y.nodeType!=1){y=y.nextSibling;}return y;}</script></head><body><script type="text/javascript">xmlDoc=loadXMLDoc("/example/xdom/books.xml");x=get_firstChild(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("book")[0]);document.write(x.nodeName);</script></body></html>
lastChild
<html><head><script type="text/javascript" src="/example/xdom/loadxmldoc.js"></script><script type="text/javascript">//check if the first node is an element nodefunction get_lastChild(n){y=n.lastChild;while (y.nodeType!=1){y=y.previousSibling;}return y;}</script></head><body><script type="text/javascript">xmlDoc=loadXMLDoc("/example/xdom/books.xml");x=get_lastChild(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("book")[0]);document.write(x.nodeName);</script></body></html>
nextSibling
<html><head><script type="text/javascript" src="/example/xdom/loadxmldoc.js"></script><script type="text/javascript">//check if the first node is an element nodefunction get_nextSibling(n){y=n.nextSibling;while (y.nodeType!=1){y=y.nextSibling;}return y;}</script></head><body><script type="text/javascript">xmlDoc=loadXMLDoc("/example/xdom/books.xml");x=get_nextSibling(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("title")[0]);document.write(x.nodeName);</script></body></html>
previousSibling
<html><head><script type="text/javascript" src="/example/xdom/loadxmldoc.js"></script><script type="text/javascript">//check if the first node is an element nodefunction get_previousSibling(n){y=n.previousSibling;while (y.nodeType!=1){y=y.previousSibling;}return y;}</script></head><body><script type="text/javascript">xmlDoc=loadXMLDoc("/example/xdom/books.xml");x=get_previousSibling(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("price")[0]);document.write(x.nodeName);</script></body></html>