Java 实例 - 获取线程状态
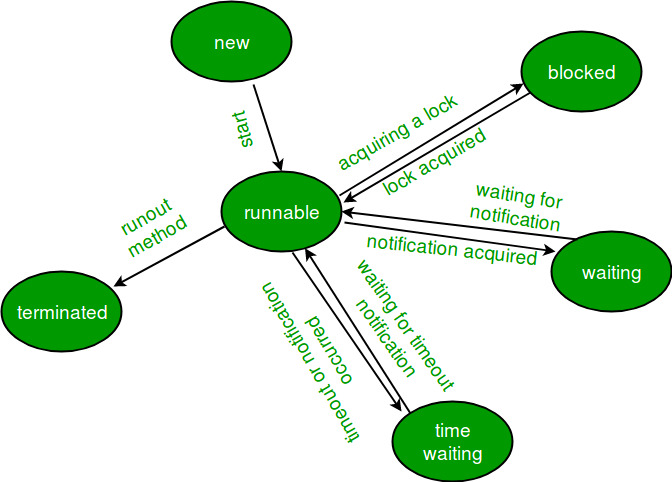
Java 线程的生命周期中,在 Thread 类里有一个枚举类型 State,定义了线程的几种状态,分别有:
- New
- Runnable
- Blocked
- Waiting
- Timed Waiting
- Terminated
各个状态说明:
1. 初始状态 - NEW
声明:
public static final Thread.State NEW
实现 Runnable 接口和继承 Thread 可以得到一个线程类,new 一个实例出来,线程就进入了初始状态。
2. RUNNABLE
声明:
public static final Thread.State RUNNABLE
2.1. 就绪状态
就绪状态只是说你资格运行,调度程序没有挑选到你,你就永远是就绪状态。
调用线程的 start() 方法,此线程进入就绪状态。
当前线程 sleep() 方法结束,其他线程 join() 结束,等待用户输入完毕,某个线程拿到对象锁,这些线程也将进入就绪状态。
当前线程时间片用完了,调用当前线程的 yield() 方法,当前线程进入就绪状态。
锁池里的线程拿到对象锁后,进入就绪状态。
2.2. 运行中状态
线程调度程序从可运行池中选择一个线程作为当前线程时线程所处的状态。这也是线程进入运行状态的唯一一种方式。
3. 阻塞状态 - BLOCKED
声明:
public static final Thread.State BLOCKED
阻塞状态是线程阻塞在进入synchronized关键字修饰的方法或代码块(获取锁)时的状态。
4. 等待 - WAITING
声明:
public static final Thread.State WAITING
处于这种状态的线程不会被分配 CPU 执行时间,它们要等待被显式地唤醒,否则会处于无限期等待的状态。
5. 超时等待 - TIMED_WAITING
声明:
public static final Thread.State TIMED_WAITING
处于这种状态的线程不会被分配 CPU 执行时间,不过无须无限期等待被其他线程显示地唤醒,在达到一定时间后它们会自动唤醒。
6. 终止状态 - TERMINATED
声明:
public static final Thread.State TERMINATED
当线程的 run() 方法完成时,或者主线程的 main() 方法完成时,我们就认为它终止了。这个线程对象也许是活的,但是,它已经不是一个单独执行的线程。线程一旦终止了,就不能复生。
在一个终止的线程上调用 start() 方法,会抛出 java.lang.IllegalThreadStateException 异常。
以下实例演示了如何获取线程的状态:
Main.java 文件
// Java 程序 - 演示线程状态class thread implements Runnable{public void run(){// thread2 - 超时等待try{Thread.sleep(1500);}catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("State of thread1 while it called join() method on thread2 -"+Test.thread1.getState());try{Thread.sleep(200);}catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}}}public class Test implements Runnable{public static Thread thread1;public static Test obj;public static void main(String[] args){obj = new Test();thread1 = new Thread(obj);// 创建 thread1,现在是初始状态System.out.println("State of thread1 after creating it - " + thread1.getState());thread1.start();// thread1 - 就绪状态System.out.println("State of thread1 after calling .start() method on it - " +thread1.getState());}public void run(){thread myThread = new thread();Thread thread2 = new Thread(myThread);// 创建 thread1,现在是初始状态System.out.println("State of thread2 after creating it - "+ thread2.getState());thread2.start();// thread2 - 就绪状态System.out.println("State of thread2 after calling .start() method on it - " +thread2.getState());// moving thread1 to timed waiting statetry{//moving - 超时等待Thread.sleep(200);}catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("State of thread2 after calling .sleep() method on it - "+thread2.getState() );try{// 等待 thread2 终止thread2.join();}catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("State of thread2 when it has finished it's execution - " +thread2.getState());}}
以上代码运行输出结果为:
- State of thread1 after creating it - NEW
- State of thread1 after calling .start() method on it - RUNNABLE
- State of thread2 after creating it - NEW
- State of thread2 after calling .start() method on it - RUNNABLE
- State of thread2 after calling .sleep() method on it - TIMED_WAITING
- State of thread1 while it called join() method on thread2 -WAITING
- State of thread2 when it has finished it's execution - TERMINATED